Time:2025-01-20
Time:2025-01-20
 Source:青绿环境
Source:青绿环境
Construction waste refers to the surplus materials, tailings, and other waste products generated during the decoration, repair, and decoration processes of various buildings. These waste materials include wood, plastic, metal, textiles, glass, gypsum, tiles, cement, and other materials, and often contain chemical substances such as paints and coatings. If not disposed of properly, it will not only lead to waste of resources, but also cause environmental pollution problems.
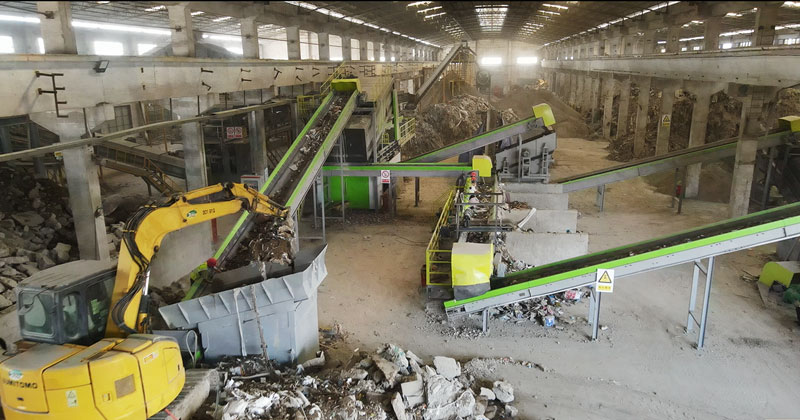
Construction Waste Processing Equipment
Demolition Waste
Definition: Waste generated during the demolition of buildings, including debris of structural materials such as walls, floors, beams, and columns.
Main Components:

- Concrete: Such as cement, bricks, and stones.
- Reinforcing Steel: Metal materials used to reinforce buildings.
- Wood: Such as old doors and windows, floors, and roof trusses.
- Glass: Windows, curtain walls, etc.
- Insulation Materials: Such as foam boards and rock wool.
Construction Waste
Definition: Waste generated during the construction or renovation of buildings, usually from surplus materials and waste during the construction process.
Main Components:
- Concrete Blocks: Excess concrete from the pouring process.
- Mortar: Surplus materials used for bricklaying and plastering.
- Formwork Materials: Such as wooden formwork, plastic formwork, and steel formwork.
- Packaging Materials: Such as cardboard boxes, plastic bags, and wire.
Renovation Waste
Definition: Surplus materials, tailings, and other waste products generated during the decoration, repair, and decoration processes of various buildings.
Main Components:
- Wood: Such as discarded wooden floors, door frames, and furniture.
- Plastic: Such as PVC pipes, plastic sheets, and window frames.
- Metal: Such as aluminum alloy doors and windows, copper wires, and nails.
- Textiles: Such as old curtains, carpets, and fabric sofas.
- Glass: Such as broken mirrors and glass partitions.
- Gypsum: Such as gypsum boards and moldings.
- Tiles: Such as broken or surplus tiles and mosaics.
- Cement: Such as remaining cement paste and mortar.
- Paints and Coatings: These substances may contain harmful chemical components, and improper disposal can cause environmental pollution.
Other Construction Waste
Definition: Waste generated during the construction process, other than the above three categories.
Main Components:
- Stone: Such as marble and granite fragments.
- Ceramics: Such as sanitary ware and ceramic tiles.
- Chemical Containers: Such as paint cans and solvent bottles.
- Electrical Equipment: Such as old lamps, switches, and sockets.
Hazards of Construction Waste
If not disposed of properly, construction waste will not only lead to waste of resources, but also cause serious environmental pollution. For example:
- Occupation of Land Resources: A large amount of construction waste accumulation will occupy valuable land resources.
- Pollution of Soil and Water: Construction waste containing heavy metals and chemical substances seeping into the soil and water can lead to soil and water pollution.
- Impact on Air Quality: Dust generated during the stacking and transportation of construction waste can affect air quality.
- Destruction of Ecological Balance: Random dumping of construction waste can destroy the natural ecological environment and affect the living environment of animals and plants.













 Prev
Prev