Time:2025-04-03
Time:2025-04-03
 Source:青绿环境
Source:青绿环境
Recycling and sorting centers for secondary resources are vital facilities for achieving waste reduction, resource utilization, and harmlessness. They employ a series of advanced equipment and technologies to sort and process mixed waste, thereby maximizing the use of resources. Below is an introduction to several key types of equipment commonly found in recycling and sorting centers for secondary resources and their functions.
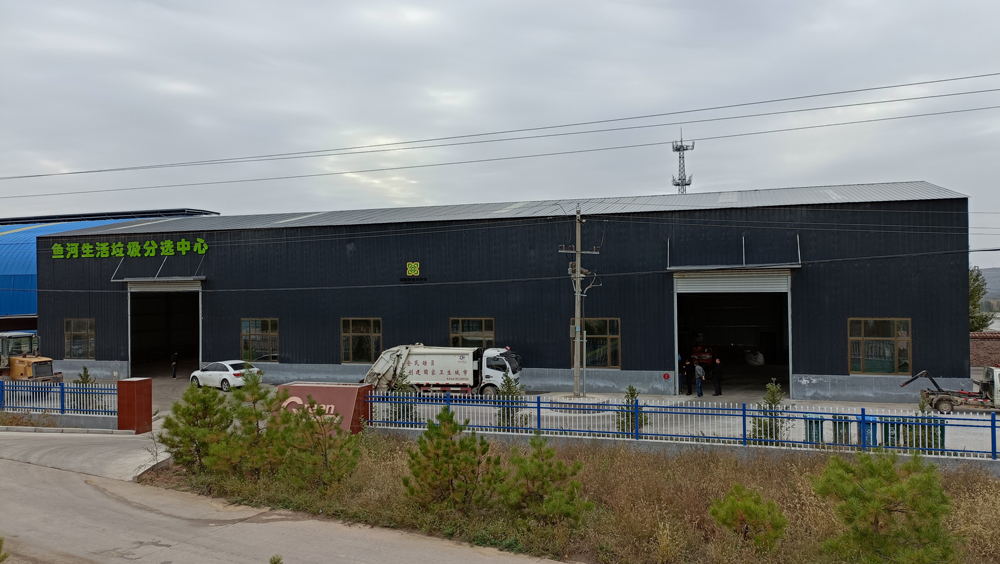

I. Feeding System
The feeding system marks the beginning of the entire sorting process. Its primary task is to efficiently and safely transport the collected waste into the subsequent processing stages. Common feeding equipment includes loaders and conveyor belts. Loaders are used to load piled-up waste onto the conveyor belts, which then evenly distribute and transport the waste to different sorting areas.
II. Crushing Equipment
To facilitate subsequent sorting and processing, large waste materials need to be crushed first. Crushing equipment mainly includes jaw crushers, impact crushers, and hammer crushers. These devices can effectively break down large waste items (such as old furniture and construction waste) into smaller particles or fragments, thereby improving sorting efficiency.
III. Screening Equipment
Screening equipment is primarily used for preliminary separation based on material size. Common types of screening equipment are vibrating screens and flat screens. Vibrating screens use motors to generate vibrations in the screen mesh, allowing materials of different particle sizes to naturally grade under the force of gravity. Flat screens rely on their inclined angle to let materials slide down and achieve separation. This type of equipment is especially suitable for handling waste containing a large amount of fine particles, such as sand, soil, and gravel.
IV. Magnetic Separators
Magnetic separators are specialized equipment for extracting ferrous metals from waste. They use strong magnetic fields to attract iron-containing substances and separate them from non-magnetic materials. Depending on their working principles, magnetic separators can be divided into two types: permanent magnet separators and electromagnetic separators. The former uses permanent magnets to generate a magnetic field, while the latter relies on an electric current to excite the coil and form a magnetic field.
V. Air Separators
Air separators utilize principles of aerodynamics to separate lightweight materials (such as plastic films and paper) from heavy materials (such as stones and bricks) using the power of airflow. When the mixture is thrown into the air, lighter items are carried away by the airflow, while heavier items fall. This method is particularly suitable for waste with significant density differences.
VI. Optical Sorting Equipment
With the advancement of technology, an increasing number of sorting centers are adopting optical sorting equipment. These devices typically combine high-resolution cameras with intelligent algorithms to identify objects of different colors, shapes, and even materials, and then precisely separate them using devices such as high-pressure air guns. For example, they can accurately distinguish PET bottles from other types of plastic products, significantly improving the purity of recyclables.
VII. Baling Machines
Finally, after all sorting is completed, various recyclables need to be compressed into bundles for transportation and storage. This is where baling machines come into play. Baling machines apply pressure to loose materials to significantly reduce their volume and form regular bales. This not only saves space but also reduces logistics costs.
Recycling and sorting centers for secondary resources rely on the coordinated operation of various specialized equipment to effectively transform waste into secondary resources. Each piece of equipment plays an indispensable role in its specific stage, collectively driving the progress and development of the environmental protection cause. With the continuous advancement of technology, more efficient and intelligent new equipment will emerge in the future, further enhancing the level of secondary resource recycling and utilization.













 Prev
Prev