Time:2025-05-09
Time:2025-05-09
 Source:青绿环境
Source:青绿环境
Designing and planning a landfill waste treatment equipment production line is a systematic and highly technical project, aimed at efficiently handling long-term accumulated domestic waste to achieve resource recovery, volume reduction, and harmlessness. Below are the key points for the design and planning of this production line:
I. Preliminary Research and Assessment
Before the design, a detailed investigation of the landfill should be conducted, including the volume of waste accumulated, waste composition analysis, moisture content, compaction degree, and site environmental conditions. At the same time, the surrounding infrastructure such as transportation, electricity, and water sources should be assessed to ensure that the project has the necessary conditions for implementation.
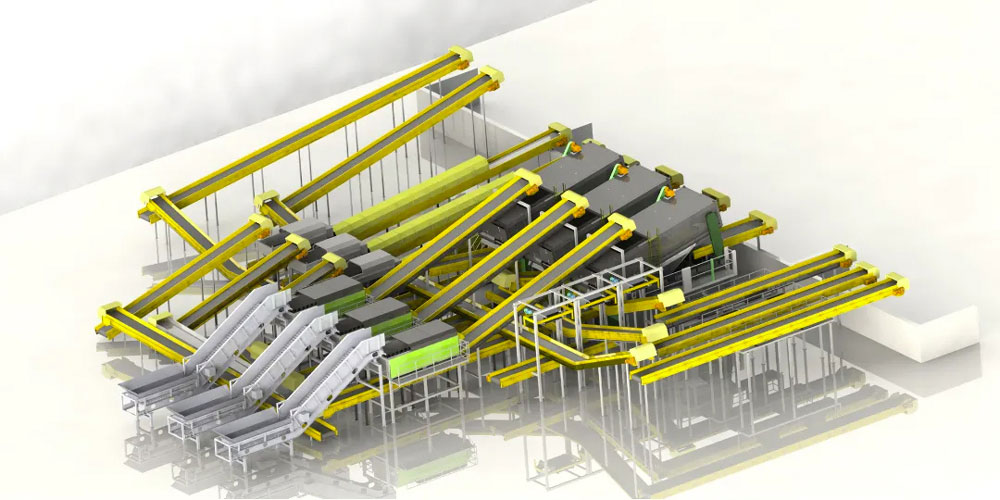
II. Process Flow Design
A landfill waste treatment production line typically includes the following core processes:
1. Excavation and Transportation: Use excavators, loaders, and other equipment to remove waste from the landfill and transport it to the pre-treatment workshop.
2. Screening Treatment: Separate waste into different particle size fractions, such as large items (plastics, textiles), organic matter, and sand and gravel, using drum screens, vibrating screens, and other equipment.
3. Separation and Recycling:
- Magnetic Separation: To separate ferrous metals;
- Eddy Current Separation: To extract non-ferrous metals;
- Air Separation or Optical Sorting: To separate light combustible materials (such as plastics, paper);
- Manual Sorting Line: For fine sorting.
4. Resource Recovery:
- Recyclables are sent to recycling plants;
- Combustible materials can be used for incineration power generation or RDF fuel production;
- Organic matter can be processed into soil conditioners or compost;
- Inorganic materials such as bricks and gravel can be used for brick making or road base materials.
5. Residue Treatment: The non-reusable part should be stabilized and safely landfilled according to regulations.
III. Equipment Selection and Configuration
Based on the processing scale (e.g., 500 tons per day), appropriate equipment models and quantities should be selected. For example:
- Drum screens;
- Multi-stage vibrating screens;
- Magnetic separators, eddy current separators;
- Air separators, optical sorting robots;
- Conveyor belt systems;
- Control systems and dust removal and odor control devices.
IV. Environmental and Safety Measures
Construct supporting facilities for wastewater treatment, exhaust gas purification (such as activated carbon adsorption + bag dust removal), and noise control. Set up fire protection, gas monitoring, and explosion-proof safety systems to ensure safe operation and environmental friendliness around the facility.
V. Plant Layout and Management
Scientifically plan functional areas such as production, storage, and maintenance, and equip them with monitoring systems and intelligent management systems to improve operational efficiency and management level.
VI. Economic Benefits and Sustainable Development
Create economic value through resource recovery and reduce operating costs. Attract social capital participation to promote the sustainable development of the waste treatment industry.
In summary, the design and planning of a landfill waste treatment equipment production line should aim for environmental protection, efficiency, and intelligence. It should be tailored to the actual situation to create a modern treatment system that integrates resource recovery and ecological restoration.













 Prev
Prev