Time:2024-11-18
Time:2024-11-18
 Source:青绿环境
Source:青绿环境
The renovation waste sorting and treatment plan is a key step to ensure that renovation waste is disposed of reasonably and utilized for resource recovery. Here is a comprehensive renovation waste sorting and treatment plan:
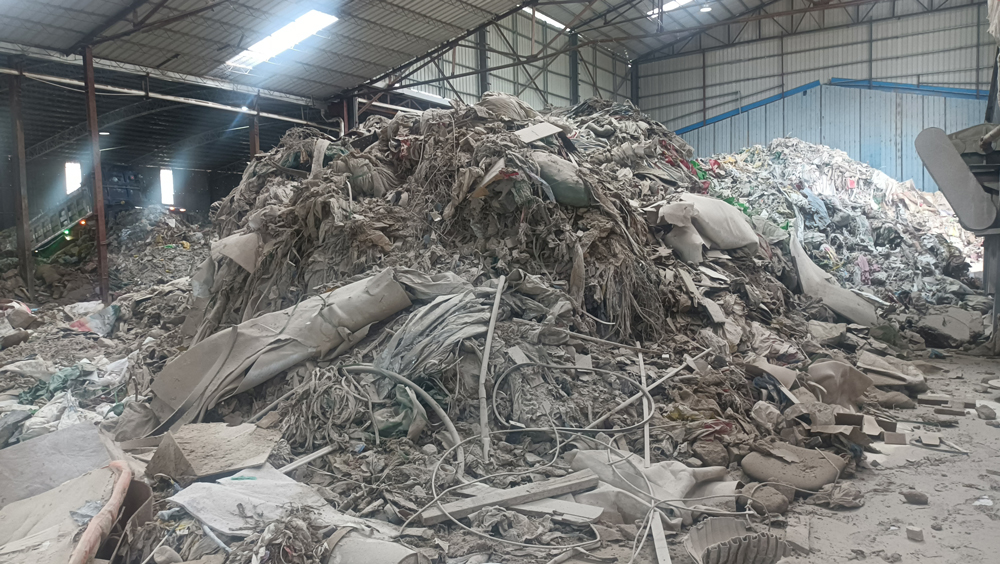

I. Sorting Principles
Renovation waste should be strictly classified into recyclables, hazardous waste, wet waste (food waste), and dry waste (other waste). This classification system helps with subsequent resource recovery and waste management.
II. Sorting Methods
Recyclables: Include waste wood, metal, glass, plastic, etc. These materials should be stored separately for subsequent recycling and reuse. For example, waste wood can be used for the manufacture of recycled wood, and waste metal can be re-smelted.
Hazardous waste: Such as paint cans, waste batteries, fluorescent tubes, etc., which require special treatment to avoid environmental pollution. These wastes should be collected separately and handed over to professional hazardous waste disposal institutions for treatment.
Wet waste: Although there is less wet waste generated during the renovation process, if there are food residues and other kitchen waste during the renovation, they should be collected separately from other waste and put into wet waste bins.
Dry waste: Such as waste gypsum board, ceramic tile fragments, waste cardboard, etc., which cannot be recycled, should be handled in accordance with local regulations. These wastes are usually transported to landfills or incineration plants for harmless treatment.
III. Treatment Process
Sorting collection: During the renovation process, different types of waste bins should be set up to guide renovation workers and residents to correctly sort and dispose of waste.
Professional transportation: Sorted waste should be transported by professional waste transportation companies to ensure that waste does not cause secondary pollution during transportation.
Resource recovery treatment: For recyclables, resource recovery should be carried out as much as possible, such as the reuse of waste wood and the recycling of waste metal.
Harmless treatment: For waste that cannot be recycled, it should be treated harmlessly in accordance with local regulations, such as landfilling or incineration for power generation.
IV. Publicity and Education
Strengthen publicity and education on the sorting of renovation waste, raise the environmental awareness of residents and renovation workers, and ensure that renovation waste is correctly sorted and treated.
By implementing the above plan, we can effectively reduce the pollution of renovation waste to the environment, achieve the recycling of resources, and sustainable development.













 Prev
Prev