Time:2024-11-19
Time:2024-11-19
 Source:青绿环境
Source:青绿环境
Waste sorting and treatment systems are efficient tools for urban environmental management, which achieve effective classification, treatment, and resource utilization of household waste through a series of advanced technologies and equipment. The working principle of this system can be summarized in the following steps:
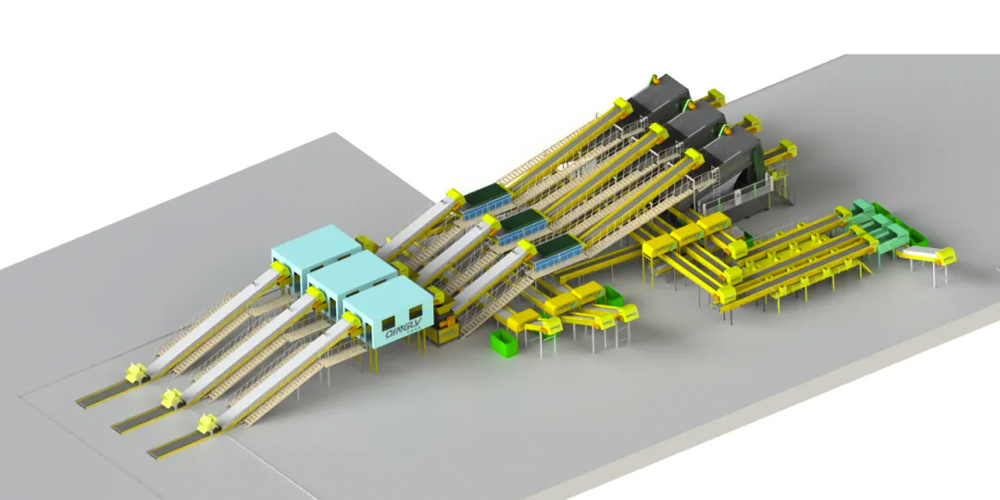
1. Collection and Transportation: Initially, residents pre-sort household waste into recyclables, hazardous waste, wet waste (food waste), and dry waste (other waste) and place them into designated trash bins. Then, specialized waste collection vehicles regularly transport these bins to centralized treatment centers.
2. Automatic Sorting: At the treatment center, waste is fed into an automated sorting line. This line typically includes conveyor belts, vibrating screens, air classifiers, and other equipment. For instance, air classifiers can separate lightweight materials such as paper and plastic from heavier ones like metal and glass based on density differences.
3. Fine Classification: For waste that is difficult to separate physically, such as precious metals in electronic waste, the system employs more sophisticated technologies like magnetic separators or X-ray fluorescence spectrometers for identification and extraction.
4. Crushing and Refinement: Large waste items, such as old furniture and appliances, are sent to crushers for pulverization to facilitate subsequent treatment and transportation.
5. Biodegradation and Transformation: Wet waste (food waste) is sent to biodegradation equipment, where it is converted into organic fertilizer or biogas through the action of microorganisms, achieving resource recycling.
6. Data Management and Optimization: The entire system is equipped with data collection and analysis modules that can monitor the operational status and sorting effects of the equipment in real-time. By analyzing large amounts of data, managers can continuously optimize the sorting process, improving overall efficiency and accuracy.
The waste sorting and treatment system, by integrating various advanced technologies and equipment, achieves efficient classification and resource utilization of household waste. This not only helps reduce environmental pollution but also promotes the development of a circular economy, making it one of the key technologies in modern urban environmental management.













 Prev
Prev